Many segments of the textile industry rely on adhesives and binders that securely hold a product together, in one way or another. From automotive, medical, hygiene and more, this seemingly invisible technology contributes to the critical success of products that are used by consumers daily. Adhesive and binding solutions are undergoing their own epiphany in the research and development to support the advancement of the products that utilize them, and industry wrestles with sustainability, durability and circularity.
IFJ highlights several companies who share their most recent news in our first edition of the IFJ Adhesives and Binding Roundup.
In today’s market, textile manufacturers strive to enhance product sustainability while meeting high performance standards such as durability, breathability, waterproofness and softness. This sustainability focus stems from needing to address regulatory and societal pressures as well as corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. However, adhesives are one component often overlooked in the sustainability journey primarily due to a lack of awareness and understanding about their impact. Instead, manufacturers may focus simply on whether the adhesive works without considering its broader impact on sustainability.
In fact, adhesives’ formulation, performance attributes and their impact at the end of a product’s life all influence textile manufacturing sustainability. By considering these elements during product development and throughout the product’s lifecycle, manufacturers can better design for sustainability.
Consider an Adhesive’s Formulation
An adhesive’s sustainability begins with its raw materials selection, which impacts chemistry selection for textile bonding applications. Water and solvent-based adhesives provide various characteristics for textile bonding; however, they can use valuable resources (water), can contain VOCs (solvent) and require energy for evaporation (waste production) that impede sustainable design.
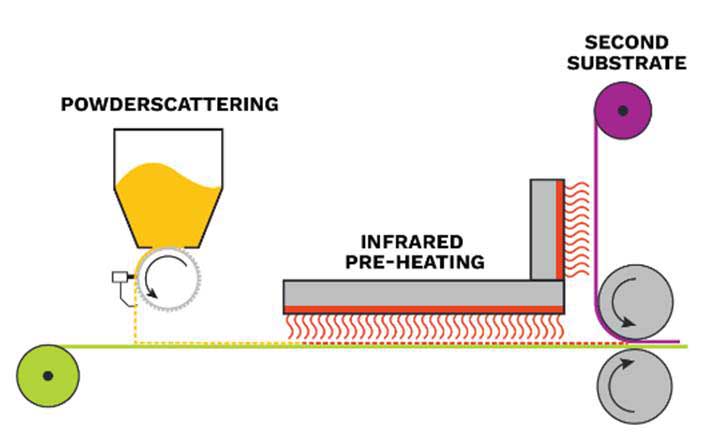
When considering sustainable design, specialty hot melt adhesives (pellets, powders, webs and films) should be explored. In addition to reducing reliance on valuable resources and VOCs, they can be based on sustainable raw material sources, such as castor beans. For example, copolyamide hot melt adhesives (castor-based) are a great choice for more sustainable launder resistant bonding applications.
Consider an Adhesive’s Performance Attributes
Historically, certain materials, such as polyurethanes, PTFE and other petroleum-based solutions have been used in the textile industry, because they possess soft hand feel, elasticity and breathability characteristics. However, when designing for sustainability, manufacturers can consider other technologies. For example, copolyester chemistries can be designed to provide soft hand feel and elastic properties similar to that of polyurethanes while bringing monomaterial design into mind for polyester textiles. Although not an adhesive, a bio-based, breathable film membrane can provide breathability and elastic properties without relying on unsustainable fluorinated chemistry in PTFE.
Our industry can benefit from a “back-to-basics” approach with an eye towards challenging our preconceptions of performance in the modern baby diaper.
Consider an Adhesive’s Ability to Influence a Product’s End of Life
Recycling and reuse of textiles are key trends in sustainable end-of-life design, and adhesives can be a factor in more complex textile products. Disassembly and monomaterial chemistry selection are common asks for all components (including adhesives) of sustainable textile design. In addition to meeting performance requirements, thermoplastic specialty hot melts can offer material separation when subjected to high heat unlike thermosetting adhesives. While polyester and nylon monomaterial textile designs mitigate the need for disassembly and enhance material reusability, these designs may be difficult to achieve due to chemistry compatibility and performance. To combat this, consider
copolyester and copolyamide adhesive chemistries. With similar raw materials, they can allow for flexibility in mechanical and/or chemical recycling.
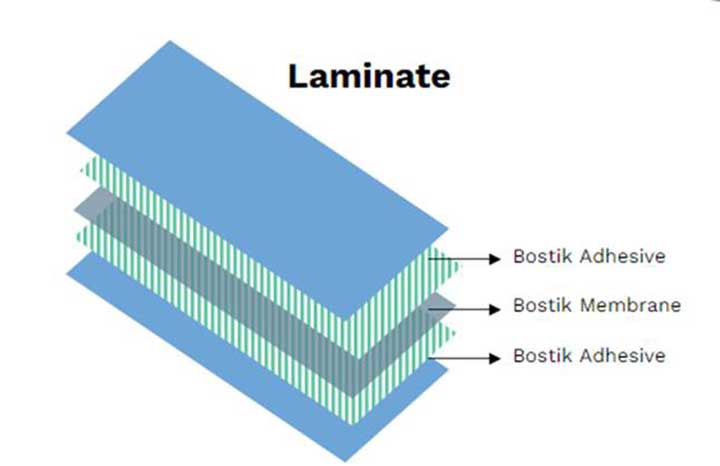
By carefully selecting adhesives based on their formulation, performance and textile end-of-life impact, manufacturers can enhance their product sustainability efforts.
As an Arkema company, Bostik offers an unmatched range of specialty hot melt copolymers (pellets, powders, webs and films) to aid in sustainable textile design. These include:
- Castor bean bio-sourced adhesives for sustainable raw material selection.
- Soft hand feel copolyesters for monomaterial design and performance.
- Arkema Pebax® membrane for a sustainable alternative to PTFE membranes.
- Thermoplastic specialty hot melts for product disassembly.
To learn how these products can help you design for sustainability and get in touch with a Bostik expert at https://tinyurl.com/munewmwn



